One Doc Entry a Day Keeps the Forum Away
-
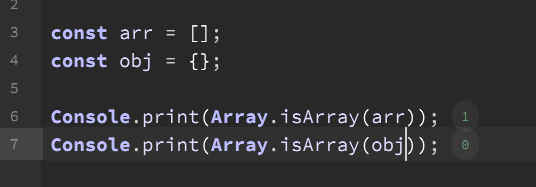
@aaronventure Lol what's the deal with Array.isArray()? It spits out the wrong value (zero) if I use it with an array and throws an error if it's not an array?
That's gotta be the least useful function in the entire API... I think I'll remove it altogether.
-
@Christoph-Hart Works here - I think you guys are using it incorrectly.
-
@d-healey Ah, yeah I looked in the source code in order to remove it but that's exactly how it works, but then Aarons example is wrong.
I also noticed that there are a few gems that are not showing up in the API - Array.filter(), Array.some() etc. which are quite powerful functions. I'll investigate.
-
@Christoph-Hart ah fuck. Alright nice, we're already making progress and we're still on the warmup class!
The show starts when we finish with the Array class.
-
Array.reverse()
Reverses the order of the elements in the array.
Array.reverse()_
const var arr1 = [1, 2, 3]; arr1.reverse(); Console.print(trace(arr1)); // [3, 2, 1] -
Array.remove()
Removes all instances of the given element.
Array.remove(var elementToRemove)const var arr1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 5,]; arr1.remove(2); Console.print(trace(arr1)); // [1, 3, 4, 5] -
Array.removeElement()
Removes the element at the given position.
Array.removeElement(int index)const var arr1 = [1, 2, 3]; Console.print(arr1[1]); // 2 arr1.removeElement(1); Console.print(arr1[1]); // 3 -
Array,sortNatural()
Sorts array of numbers, objects, or strings with "number in string" priority. Can also sort a combination of all types
Array.sortNatural()It puts arrays first in index order (doesn't sort them), followed by a mix of int, double and string variables. If a string starts with a number, it'll get thrown in the mix.
JSON objects go last.
const var arr1 = [5.2, 3, "1", "17", [4, 2], [1, 12], "word", "with2", "3LittlePigs", {"prop1": 12, "prop2": 55}]; arr1.sortNatural(); Console.print(trace(arr1)); // [[4, 2], [1, 12], "1", 3, "3LittlePigs", 5.2, "17", {"prop1": 12, "prop2": 55} ] -
Array.pushIfNotAlreadyThere()
Adds the given element at the end and returns the size.
Array.pushIfNotAlreadyThere(var elementToInsert)The method will not add an element to an array if a matching element already exists inside the array. If an argument is an element that already exists, the return will still be the first index beyond the end of an array (not an index of a first/any matching element).
const arr1 = [0, 1]; arr1.pushIfNotAlreadyThere(2); Console.print(trace(arr1)); // [0, 1, 2] // It won't add an element if it already exists in the array arr1.pushIfNotAlreadyThere(2); Console.print(trace(arr1)); // [0, 1, 2] arr1.pushIfNotAlreadyThere(1); Console.print(trace(arr1)); // [0, 1, 2] Console.print(arr1.pushIfNotAlreadyThere(1)); // 3 -
Array.map ()
Calls the given function for every array element, and returns an array of individual function returns.
Array.map(var testFunction, var optionalThisObject)The function takes one argument: the element it's currently processing. This is useful if you want to perform an operation for every single element of an array by passing in a premade function.
An alternative would be to use a
for(x in array)loop, but the map method allows for cleaner multidimensional processing.const arr1 = [0, 1]; arr1.map(function(element) { Console.print(element); });Interface: 0 Interface: 1The method returns an array of individual function returns. If no return exists, the element will be undefined/null.
const arr1 = [0, 1]; const arr2 = arr1.map(function(element) { return element + 10; }); Console.print(trace(arr2)); // [10, 11]I think that the
optional thisis broken, or I'm just not using it correctly (even though this is how it's used for other methods):const test = 10; const arr1 = [0, 1]; arr1.map(function(element) { Console.print(this); // error: API call with undefined parameter 0; }, test); -
Array.clone()
Return a clone of the array, instantiating a separate data set in the memory.
Array.clone()If you assign an array object reference to another constant or variable, you're only setting the reference. Making any changes to the array B by referencing it will also make changes to array A. If you need a separate set of data to work on, you need to clone it.
const arr1 = [0, 1]; var arr2 = arr1; // Changing any element in arr2 will also change it in arr1 arr2[0] = 22; Console.print(trace(arr1)); // [22, 1] // Reset the element 0 back to 0 arr1[0] = 0; // Cloning the array creates a new dataset in memory, separate from the original array arr2 = arr1.clone(); Console.print(trace(arr1)); [0, 1] arr2[0] = 22; Console.print(trace(arr2)); [22, 1]Because arrays in HISE are effectively objects (which is hinted at by them having a bunch of class methods we're looking at here), this method will also work with any other object, including JSON objects, component references etc.
-
Alright, this is about done. Onto the fun stuff.

-
AUDIOFILE
https://docs.hise.dev/scripting/scripting-api/audiofile/index.html
This is mostly covered, with only two methods
 linkTo
linkTo loadFile
loadFile
loadFile()is covered in the beginning of the chapter, so we can just paste the example from there// Load the example assets FileSystem.loadExampleAssets(); // Grab whatever asset is first const var firstAsset = Engine.loadAudioFilesIntoPool()[0]; Console.print(firstAsset); // {PROJECT_FOLDER}breakbeat_44k.wav // Create a audio file slot const var audioFile = Engine.createAndRegisterAudioFile(0); // load the first asset audioFile.loadFile(firstAsset);For linkTo, I have no idea what it does. How is it different than just assigning the reference? Does it let you have another audiofile, and linking it will then have it react to the callbacks of the linked audiofile?
-
Array.filter()
Creates a new array filled with elements that pass the function test.
Array.filter(var testFunction, var optionalThisObject)The function needs one argument which will be a reference to the array element. If returned
true, the element will be pushed to the array to be returned by the method.const arr = [1, 2, 3, 1]; const arr2 = arr.filter(function(element) { if (element == 2 || element == 3) return true; }); Console.print(trace(arr2)); // [2, 3]